raditional Chinese Medicine decreases COVID-19-induced mortality and hospital stays: What physicians need to know
New Harmony Center for Health and Wellness has developed a range of treatments for COVID-19 based on current research on the use of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 in China.1 Herbal medicine, in conjunction with current conventional treatments, has been proven to be more effective in decreasing mortality rates and the length of hospital stays than conventional medical treatment alone (see Yang, et al).2 TCM has also been useful for boosting immunity to this specific virus for caretakers and health care professionals (ibid.). The origin of the disease in Wuhan, China, and the decision by the Chinese government to supplement conventional medical approaches with Traditional Chinese Medicine as of March 1, 2020, provides an excellent opportunity to examine the efficacy of TCM in treating COVID-19. Over 300 clinical trials are underway, and dozens of peer-reviewed research articles have begun to publish the results. As an acupuncturist and an herbalist with over twenty years of experience in Traditional Chinese Medicine, I have been following this research. This blog post explains to doctors and other health care practitioners how and why TCM is so effective against the virus in conjunction with Western medicine, and directs them to recent peer-reviewed research for further reference. Meanwhile, New Harmony Center has begun successfully treating cases of COVID-19 via telemedicine. We are ready to collaborate with doctors who are treating patients in the current pandemic.
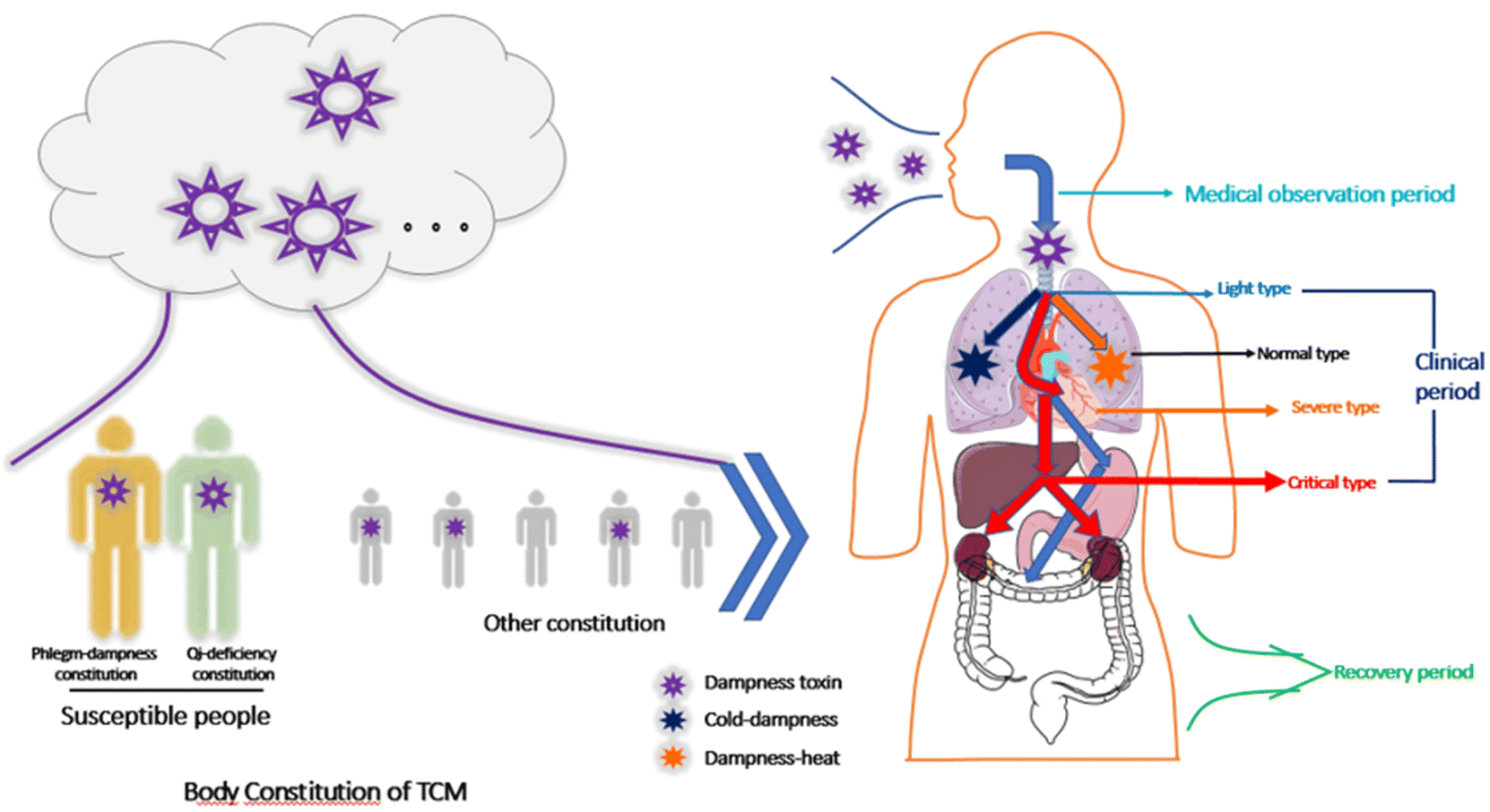
COVID-19 has proven to be very difficult to treat with Western medicine, for various reasons. The first is that there is no specific antiviral medication yet proven to be universally effective against the virus. Another challenge results from the fact that symptoms of COVID-19 and the various complications it creates differ from patient to patient. Furthermore, the disease also moves through different phases, each of which may have different manifestations. Traditional Chinese Medicine is useful because it recognizes the patterns behind each of these different manifestations and from recent corona virus outbreaks, has found it can treat various aspects of COVID-19. On one level, herbs work to prevent the invasion of the virus through the cellular wall, thereby interrupting its replication.
TCM has another strength in that treatment can focus on any of the various aspects of how a COVID-19 infection manifests. TCM is able to differentiate between manifestations of how the body is defending itself, or patterns of physiological response. In beginning stages, supporting the body’s immune response is focused more at the surface, as the pathogen is entering the body. In differentiating treatment approaches for the more severe pneumonia phase, a deeper Shaoyang Syndrome w/ Damp, or Damp Heat afflicting the lung is identified, which may be combined with a Toxic Stagnation identified as obstructing the lungs. Formulas are written to address the physiological syndrome manifesting in the lungs, in conjunction with treating the virus as a target, per se.3
Traditional Chinese Medicine and conventional Western medicine used together offer the most effective treatment for COVID-19.
One challenge in treating COVID-19 with Western medicine is the two distinct phases of the virus, with a period of seeming recovery in between, and the long asymptomatic incubation period that precedes the manifestation of viral symptoms. Yang, et al’s research on the success of TCM in treating COVID-19 demonstrates that “some patients with mild illness in the early stage could suddenly progress to severe disease, and eventually died due to septic shock with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), which was associated with cytokine storm. There is compelling evidence that some TCM herbal products or its components have potent immunosuppressive effects.” Yang, et al begin the paper by linking the current treatment to previous approaches to treating SARS. They cite, for example, that the mortality rate from SARS in Beijing “was initially more than more than 52% until the 5th of May and decreased gradually to 4%-1% after the 20th of May in 2003. The dramatic reduced fatality from late May in Beijing was believed to be associated with the use of TCM as a supplement to the conventional therapy”. They then discuss, in very specific ways, how COVID-19 works and how TCM interrupts viral cellular entry, absorption, and penetration. They also explain how TCM works as anti-inflammatory agents that mitigate the overwhelming inflammatory responses that cause the deaths by COVID -19. While the paper reports very specific results of success using TCM in combination with conventional Western medicine, and provides a list of formulas used, they also point to the use of TCM in prevention (Yang, et al (2020)).
Wan, et al also describe useful integration of Chinese-Western medicine in treating COVID-19, with the specific recommendation that “patients should be treated by a combination of Western and Chinese medicines. Compared to the mild cases, the severe ones had lower lymphocyte counts and higher plasma levels of Pt, APTT, d‐dimer, lactate dehydrogenase, PCT, ALB, C‐reactive protein, and aspartate aminotransferase.”4 Fui Fui Lem, et al, contribute with a review of 160 research articles to analyze information about “six drugs (ritonavir, lopinavir, oseltamivir, remdesivir, favipiravir, and chloroquine) in combination with three traditional Chinese medicines (Shuang Huang Lian Kou Fu Ye, TCM combination of Bu Huan Jin Zheng Qi San and Da Yuan Yin, Xue Bi Jing Injection and Qing Fei Pai Du Tang)”.5 In another study, Ren, et al, in an examination of over 60,000 cases, evaluates the use of TCM by thousands of medical staff dispatched to Hubei province. The study reports an over 90% cure rate, decrease in length of hospital stays, reduction in the rate of severe cases, and a 70% increase in lymphocyte counts. The article describes the Qingfei Paidu Decoction (QPD) used in the treatment and provides specific recommendations for treatment protocols.6
Qingfei Paidu Decoction was also used to treat COVID-19 in a hospital in Wuhan (Luo, et al). As in Hubei province, the treatment also involved other formulas, including compound quercetin, luteolin, kaempferol, and acacetin. The study demonstrates success in QPD and Chinese NHC-recommended formulas in the recovery of the disease in varied disease progresses. Another insight from Luo, et al, however “suggest[s] the importance of regulating intestinal function and keeping microenvironmental balance in TCM treatment of NCP (novel coronavirus pneumonia)”7 Indeed, the role of bacteria has emerged in research indicating that a specific bacteria genus may be involved in “increasing the virulence” of the virus. A review article published on Plum Dragon Herbs reviews recent peer-reviewed research on the role of bacteria in complicating cases of COVID-19, and explains how Traditional Chinese Medicine can address this specific problem.8
Another decoction, Lianhuaqingwen, has been useful for treating the COVID-19 virus (for a discussion of recent use in hospitals see the preprint by Han, et al, in note 2). However, much of the research on this treatment so far is based on lab studies.9 Those approaches are drawn, however, from the proven effectiveness of Linhuaqingwen for treating the H1N1 virus, which has similarities to the COVID-19 virus.10
In summary, these and other recent research publications point to the need for doctors and nurse practitioners treating COVID-19 patients in the United States to consider amplifying their treatment with the medications proven successful in treating the virus in China. An experienced practitioner of Traditional Chinese Medicine will be able to consider the specific herbal formula necessary to meet the needs of each individual patient. At New Harmony Center for Health and Wellness, we can conduct these evaluations via telemedicine, and we have all the medicines in stock in our herbal dispensary. We look forward to collaborating with you! Give us a call at 978 922-3030 or email Bryn Clark at bryn@newharmonywellness.com.
For an overview of TCM treatments, see: Huan-Tian Cui, Yu-Ting Li, Li-Ying Guo, Xiang-Guo Liu, Lu-Shan Wang, Jian-Wei Jia, Jia-Bao Liao, Jing Miao, Zhai-Yi Zhang, Li Wang, Hong-Wu Wang, Wei-Bo Wen. Traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of coronavirus disease 2019: a review. Traditional Medicine Research, 2020, 5(2): 65-73. doi: 10.12032/TMR20200222165. Kam Wa Chan, Vivian Taam Wong, Sydney Chi Wai Tang. COVID-19: An Update on the Epidemiological, Clinical, Preventive and Therapeutic Evidence and Guidelines of Integrative Chinese–Western Medicine for the Management of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Vol. 48, No. 3, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X20500378. See also Ren, et al, cited below. []Yang Y, Islam MS, Wang J, Li Y, Chen X. Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Patients Infected with 2019-New Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A Review and Perspective. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(10):1708–1717. Published 2020 Mar 15. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45538. See also Han, et al: “Studies available in Chinese and English were included in the searches and extracted. The total number of exposed patients in all 195 clinical studies from the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry amounted to 24,500. In the secondary analysis, treatment with Lopinavir-ritonavir and treatment with Hydroxychloroquine was not associated with a difference from standard of care in the rate of RT-PCR negativity; treatment with a combination of Lopinavir-ritonavir, interferon α, and Lian-Hua-Qing-Wen capsule was found to significantly improve the effective rate of treatment compared with Interferon α combined with Lian-Hua-Qing-Wen capsule.” Han, R.; Wang, Y.; Dabbous, M.; Liang, S.; Qiu, T.; Toumi, M. Chinese Clinical Studies for Pharmacological Treatments of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Preprints 2020, 2020040279 (doi: 10.20944/preprints202004.0279.v1 [*the Han, et al preprint is not peer-reviewed]). []See Xu et al for an excellent, lucid description of how TCM understands the lungs and various specific formulas to treat mild or severe infections and how they work on the lungs. Jia Xu, Yunfei Zhang, Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment of COVID-19. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice. Volume 39, 2020, 101165, ISSN 1744-3881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101165. (http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1744388120303066) []Wan S, Xiang Y, Fang W, et al. Clinical Features and Treatment of COVID-19 Patients in Northeast Chongqing. J Med Virol 2020: 1-10. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/jmv.25783 []Fui Fui Lem, Fernandes Opook, Dexter Lee Jiunn Herng, Chin Su Na, Fahcina P Lawson, Chee Fong Tyng. Molecular mechanism of action of repurposed drugs and traditional Chinese medicine used for the treatment of patients infected with COVID-19: A systematic review. medRxiv 2020.04.10.20060376; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.10.20060376 []“From current treatment… TCM based on an over-all symptoms of 2019-nCoV pneumonia patients, has suggested to prescribe prescription[s] … such as Qing Fei Pai Du decoction (QPD), Gan Cao Gan Jiang decoction, She Gan Ma Huang decoction, Qing Fei Tou Xie Fu Zheng recipe, etc. QPD which consisted of Ephedrae Herba, Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma Praeprata cum Melle, Armeniacae Semen Amarum, Gypsum Fibrosum, Cinnamomi Ramulus, Alismatis Rhizoma, Polyporus, Atractylodis Macrocephalae Rhizoma, Poria, Bupleuri Radix, Scutellariae Radix, Pinelliae Rhizoma Praepratum cum Zingibere et Alumine, Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens, Asteris Radix et Rhizoma, Farfarae Flos, Belamcandae Rhizoma, Asari Radix et Rhizoma, Dioscoreae Rhizoma, Aurantii Fructus Immaturus, Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium, and Pogostemonis Herba … in the diagnosis and treatment plan of COVID-19 in China.” Ren JL, Zhang AH, Wang XJ. Traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 treatment [published correction appears in Pharmacol Res. 2020 Mar 25;:104768]. Pharmacol Res. 2020;155:104743. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104743 []“Comparing the hemograms between admission and discharge of hospital, the number of leukocytes, neutrophil, lymphocyte and platelet increased, while the numbers of erythrocytes, hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit decreased. According to the standard coefficients of regression, the factor affecting the length of stay for the most was CMs in the category of invigorating spleen and removing dampness (ISRD), followed by administering CMs, male, and cough. Thirty-two CMs were screened after deleting duplication from QFPDD and NHC-recommended formulas. on the compound level both in generality and individuality.” Luo, E., Zhang, D., Luo, H. et al. Treatment efficacy analysis of traditional Chinese medicine for novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19): an empirical study from Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. Chin Med 15, 34 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-020-00317-x []www.plumdragonherbs.com/blogs/news/bacterial-genus-increasing-virulence-of-covid-19-revealed-explained []Runfeng L, Yunlong H, Jicheng H, et al. Lianhuaqingwen exerts anti-viral and anti-inflammatory activity against novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 20]. Pharmacol Res. 2020;156:104761. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104761. See also Ding Y. The Chinese prescription lianhuaqingwen capsule exerts anti-influenza activity through the inhibition of viral propagation and impacts immune function. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017;17(1):130). []Duan, Zhong-ping; Jia, Zhen-hua; Zhang, Jian; Liu, Shuang; Chen, Yu; Liang, Lian-chun; Zhang, Chang-qing; Zhang, Zong; Sun, Yan; Zhang, Shu-qin; Wang, Yong-yan; WU, Yi-ling. Natural herbal medicine Lianhuaqingwen capsule anti-influenza A (H1N1) trial: a randomized, double blind, positive controlled clinical trial. Chinese Medical Journal: September 2, 2011 – Volume 124 – Issue 18 – p 2925-2933. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2011.18.024. Current approaches are based on the long study of the treatment of similar viruses in TCM: Luo, H., Tang, Q., Shang, Y. et al. Can Chinese Medicine Be Used for Prevention of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)? A Review of Historical Classics, Research Evidence and Current Prevention Programs. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 26, 243–250 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-020-3192-6. []